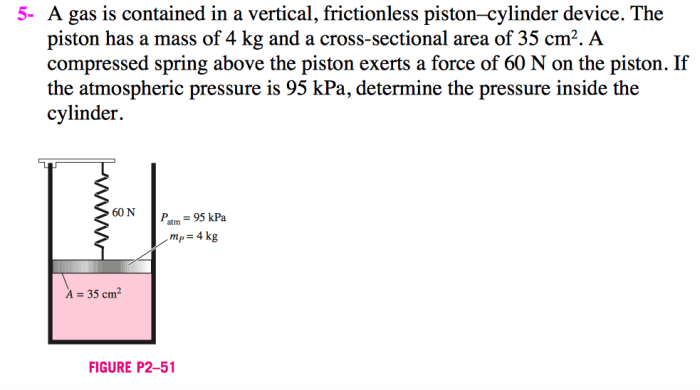
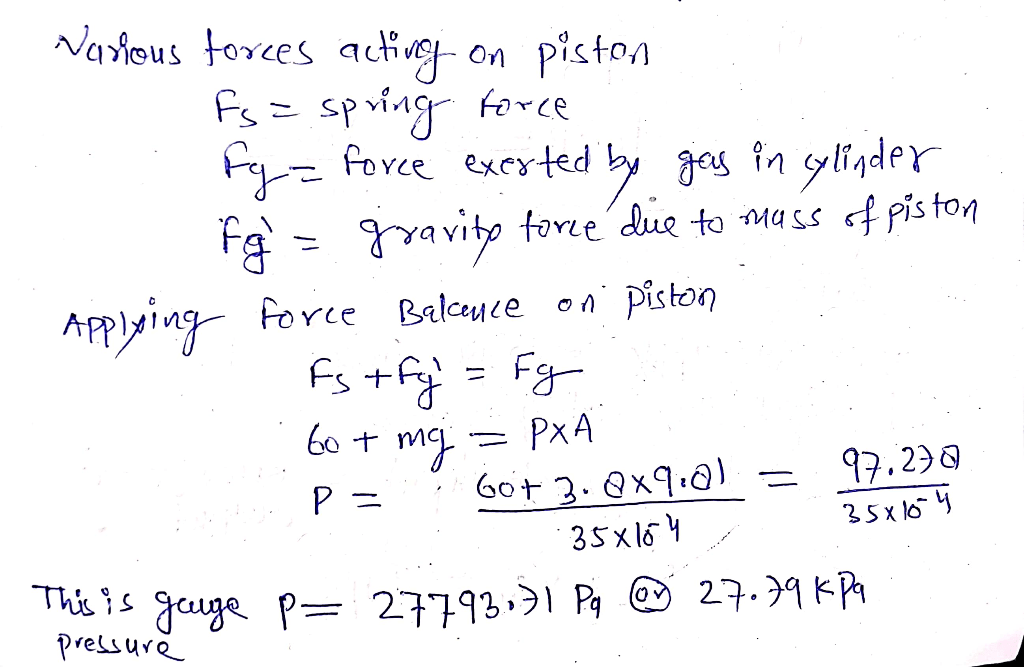A gas is contained in a vertical frictionless piston-cylinder device – A gas contained in a vertical frictionless piston-cylinder device provides a unique platform to explore the fundamental principles of gas behavior and thermodynamics. This system allows for controlled manipulation of pressure, volume, and temperature, enabling a deeper understanding of gas properties and their applications.
The behavior of gases in such a device is governed by the ideal gas law, which establishes a relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature. This law serves as a cornerstone for understanding gas dynamics and forms the basis for various gas laws, including Boyle’s law, Charles’s law, and the combined gas law.
1. Gas Properties and Behavior
Gas, one of the four fundamental states of matter, exhibits unique properties and behaviors that are essential to understand in various scientific and engineering disciplines. This section explores the fundamental relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature of gases, introducing the concept of the ideal gas law and its significance.
Additionally, we will delve into different gas laws and their practical applications.
1.1. Relationship between Pressure, Volume, and Temperature, A gas is contained in a vertical frictionless piston-cylinder device
The behavior of gases is governed by three fundamental properties: pressure, volume, and temperature. These properties are interrelated and can be described by various gas laws, such as Boyle’s law, Charles’s law, and the combined gas law. Boyle’s law states that at constant temperature, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume, while Charles’s law states that at constant pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature.
The combined gas law combines these two laws, providing a comprehensive relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature.
1.2. Ideal Gas Law
The ideal gas law is a fundamental equation that describes the behavior of an ideal gas, a theoretical gas that obeys the assumptions of kinetic molecular theory. The ideal gas law states that the pressure, volume, and temperature of an ideal gas are related by the equation PV = nRT, where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is the temperature.
This law provides a valuable tool for predicting the behavior of gases in various conditions.
1.3. Gas Laws and Their Significance
In addition to the ideal gas law, there are several other gas laws that describe the behavior of gases under specific conditions. These laws include Dalton’s law of partial pressures, which states that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of non-reacting gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas, and the law of corresponding states, which relates the behavior of different gases under similar conditions.
FAQ Section: A Gas Is Contained In A Vertical Frictionless Piston-cylinder Device
What is the significance of a frictionless piston in this system?
A frictionless piston eliminates frictional forces, allowing for ideal gas behavior and precise control over volume changes.
How does the ideal gas law apply to this system?
The ideal gas law provides a mathematical relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature, enabling the prediction of gas behavior under various conditions.
What are the practical applications of studying gas behavior in this system?
Understanding gas behavior in piston-cylinder devices has applications in engine design, refrigeration systems, and gas compression technologies.